Frequently asked questions
The application is free to download from the App Store for mobiles /tablets working with iOS sytsem or Google Play for mobiles/tablets working with Android system.
When you start the application you need to create a user profile, at least with your name. You have the option to take the recording anonymously, as well.
For you to get the most accurate results out of the functions, you need to give as much personal details as you can throughout the creating of the profile or in the profile menu.
After these the application is ready to use, you can get further instructions from the application or our website.
In the application you need to choose „New recording”.
Please follow the instructions and turn on the WIWE device. You need to make sure that Bluetooth connection is turned on on your smartphone /tablet.
You need to choose the WIWE device out of the available devices.
After these please follow the instructions given to you and start the recording.
You can share the recording from the evulation screen.
Getting into the share function, you can choose from existing contacts or you can type in a new one. In the latter case you have to give the person’s name and e-mail address or you can add one from your contact list.
To use the pedometer you’ll need the accelaration sensor built-in the WIWE, so you need to have WIWE with you.
You can switch on the pedometer in the settings menu of the application.
The function itself and the measured data/results are accessible in the data menu/fitness.
The number of profiles created on the application is not limited, it depends only on the storage capacity of your phone/tablet.
Yes, you have the possibility to log into your profile with your Facebook or Google+ profile.
The Cloud service is not yet implemented in the application, but you can easily share the recordings automatically with the chosen peolpe in e-mail format by setting it up in the „share” funcion.
The measurement results are sent as a PDF attachment.
If there is(are) one or more yellow sign(s) on the evaluation screen, please repeat the recording within 5 minutes.
If there is(are) one or more red sign(s) on the evaluation screen, please repeat the recording immediately. If the sign shows red again, contact your GP or cardiologist.
There is no known limit in the recording of the heart rate, so WIWE can give accurate results in the highest pulse threshold, too.
One recording takes 60 seconds, which is enough time to make significant results.
WIWE cannot be used for continuous monitoring, it is meant to record short ECG waves.
If the user has a pacemaker with ventricular pacing, the electric impulse propagating through the ventricles uses a different pathway than usual (without pacemaker). Consequently, the ventricular activation wave (QRS complex) can change significantly, both in terms of morphology and amplitude, on the ECG. During the automatic ECG processing, each cardiac cycle is identified by the corresponding QRS complex. Therefore if, for example, the amplitude of these waves decreases under a certain limit, the ECG processing software of WIWE might not be able to evaluate the pacemaker record.
Recording is suggested to be carried out in relaxed circumstances. If possible, during the recording sit relaxed, breath steadily, don’t speak or move. Any muscle movement might disturb the recording process.
If the recording doesn’t start, then you need to check, if Bluetooth is on and your phone or tablet is connected to WIWE.
When this part is done, please follow the instructions the application gives you.
If the battery is flat, you can charge WIWE with a microUSB cable. A red LED will show that it’s charging until it switches off.
It is suggested that you place your phone at least 30 cms (cca. 1 ft) distance from WIWE during recording.
During the usage of the application the distance between WIWE and phone/tablet should be maximum 10 meters (cca. 33 ft).
No, the communication between your phone/tablet and WIWE is using Bluetooth, so you won’t need internet connection. Your results will be stored on the phone/tablet.
If you want to share your recordings though, you will need some kind of internet connection.
You will only need WIWE to take recordings, it will store the data in its own memory.
To check the results you will need to use the WIWE application, which you can download to many Android and iOS devices for free.
For further information please check our compatibility list here
You can send your ECG recording to your doctor through the built-in share function in the application.
Also, you can send your ECG recordings to anyone else from your smartphone’s contact list or you can type in a new e-mail address.
Please take recordings 3 times a week in case the measured data is in the the normal value range.
Should your results often show data out of the normal value range or should you experience fast heart beating, fluttering in the chest, shortness of breath, it is recommended to take a measurement with WIWE which you should send to your doctor along with a description of your symptoms.
In case the following symptoms are severe, please seek medical advice first before taking a measurement with WIWE.
Yes, of course, your family members can use it too.
With WIWE you can create different user profiles in the application, so you can store data separately.
Anyone can use WIWE to record ECG, although the algorithm which calculates the risks is optimized for at least 18 year old adults. Considering this, the evaluation for anyone younger than 18 won’t be 100% correct.
Instructions for using WIWE can be found on the website's "How to use" page. There is also a Getting started guide in the application which walks you through the first steps needed for using WIWE.
If, by applying the proper measuring technique, you regularly get red patches in your assessment, it is advisable to show your results to a cardiologist eitheir via email or in printed format. WIWE's assessment results need to be further assessed by a medical professional and if he/she sees it fit, he/she will start the prescribed protocoll to diagnose your problem.
Yes, you still need to see the doctor. WIWE can’t replace medical care, it enables you to check your hearts functioning.
You will have the opportunity to make a recording with WIWE if you do not feel well and send it to your doctor rigth away or show him/her later.
Things to do before using WIWE
A) In case of normal recording
After unpacking WIWE, you need to download (you can do it here) the necessary mobile application, and pair your mobile and the WIWE. After that, turn on WIWE with the power button on the top right side of the device, then in case of proper battery charge you can use it immediately.
B) In case of occasional recording
When your mobile phone is not available, you can also take an occasional recording. By occasional recording use only the WIWE during recording in which case the data is stored on the device itself. You will be able to check the evaluation of this recording (identified with a time stamp), when you do the next synchronization with your mobile phone.
Downloading and setting up the application
WIWE is ready to use after creating your profile and pairing your mobile phone and the WIWE through Bluetooth connection. It is suggested for you to make a profile, but you have the possibility to take recordings anonymously, independently of your profile.
Pairing phone and WIWE
- Both the WIWE and your mobile phone need to be turned on to set up the connection.
- Turn on the Bluetooth connection on your phone.
- Push the I/O button to turn on the WIWE. If it connects properly with your phone then the application will detect the WIWE automatically in the future in case of a new recording.
- You can pair the WIWE and your mobile phone later as well, when you start a new recording.
- Throughout pairing the WIWE and your phone need to be in range of each other for the Bluetooth connection.
Before usage
Please, check the following conditions before each recording with WIWE to ensure proper operation:
• The integrity of the device. Make sure that the product is in good condition and not damaged.
• The sensors have to be clean.
• The state of the battery.
When all 4 LEDs are glowing on the top of the device, then it is fully charged. The glowing of 1 LED means that the battery is charged for 25%. If there are less than 2 LEDs glowing, then you need to charge the device before usage. (For detailed instructions about charging, please check the corresponding chapter).
What you need to do if you experience issues in the device’s performance or functioning.
There are two developer functions that are good to be aware of:
- Hard reset: press and hold the I/O button for 10 seconds to reboot WIWE if you experience connectivity issues, or the device freezes
- Data deletion: plug your WIWE device to a micro-USB charger and press the I/O button fives times in quick succession
The WIWE is designed for long-lasting, proper performance. If you have any complaints, please contact our Customer Service. (info@myWIWE.com).
Effects related to home usage
WIWE requires the same treatment as any other electronic home device. Please, do not store it in wet environment. Avoid strong electromagnetic fields, do not put WIWE on speakers, microwave ovens or close to similar electronic devices. It does not require any special storage and handling procedures.
A pedometer is a portable electronic or electromechanical device, which counts the steps you take by detecting the movement of your hands or hips.
The WIWE device has a built-in pedometer function.

It’s enough to carry the WIWE (you can learn more here about usage) with you and thanks to its accelerometer while in sleep mode WIWE will continuously count the steps you take.
- Stores your data on a daily / weekly / monthly / yearly breakdown and summarizes the distance you have taken
- It calculates the calories you have burned
- You can follow your activity on graphs and pie charts shown by fixed figures or percent sign.
Rewards
Depending on how much you have reached compared to your goal (10.000 steps is the daily advised number), in the mid of the pie chart there will appear a picture of barefoot/slippers/sandals/shoes/training shoes.


Results
Shows motivating milestones
Data
To have a more accurate functioning, give detailed personal information in the application (gender, age, height, weight).
From the given data the application calculates the BMR and BMI.
BMR means Bassal Metabolic Rate. This is the amount of energy which your body burns (uses) during resting (status without any physical effort) for the maintenance of physiological functions. This is 60-70% of our daily calorie need. It includes breathing, heart beating, sweating, the maintenance of body temperature and functioning of other organs, etc.
BMI (Body Mass Index=rate of body weight and height) By measuring Body Mass Index, sport and nutritional doctors and experts can determine the extent of obesity and by that the possible risks for your health.
Daily goal: When you determine your daily goal, the number of steps, the distance and the burned calories will appear. If you set any target data, the other two data will be assigned automatically.
Notifications
You will get an automatic message when you reach 80% or 100% of your goal and in case you get a new hint.
Hints
To follow your current activity, you will recieve actual hints in the form of automatic messages.


Additional guide for the proper SPO2 recording technique
During the recording with the WIWE device, the spo2 measurer ’s led (in the left-sided sensor) should be red: if this red light can be seen, the spo2 is supposed to have no functional default. ( spo2’s led is red only till the spo2 result is given)
Please note that during the assembly of WIWE, it goes through a functional investigation with regards to its main parts, of which investigation spo2 sensor is part.
The fact of having no spo2 result is probably due to the not adequate signal quality. Signal quality can be approved by knowing the proper method of recording. This will result in having punctual results in case of either SPO2-measuring and ECG parameters.
The proper, relaxed positioning of fingers, the proper humidity value, and the proper blood circulation all might influence the result of the SPO2 recoring.
In details:
1. Blood circulation: proper blood circulation in the fingers is a condition of determining spo2. If blood circulation is not proper, then the fingers are cold. In this case, please massage your palms and fingers.
2. Humidity: to have a proper humidity is also important. If the fingers are too dry, spo2 measuring will be not appropriate. In this case please make your fingers slightly wet.
3. Relaxed positioning of arms and fingers:
- please place the WIWE on the table and place your index fingers on the sensors in a way that your wrist and even your elbow is supported by the table, and palms are relaxed close to the WIWE. This is the most effective way of having a relaxed positioning of arms and fingers.
- do not press the sensors – it is totally enough only to touch the sensors with your fingertips (the very end of your fingers, where the stimulus is the most effectively detectable).
- try to touch the sensors with the biggest possible surfuce of fingertips
- be sure that the fingers of your left hand does not touch the fingers of your right hand.
If you try to fix your fingers that way, that will most probably help to develop your technique of measuring and you will get the needed results of SPO2.
If you have the chance to give further feedback on the above points, that would be appreciated.
1. Proper method of ECG recording
The recording of the ECG needs a stabile positioning of the hands/ fingers so that WIWE can give an
evaluated and proper record. Our request is to try to improve the technique of recording so as to
have punctual results in case of either SPO2-measuring and ECG parameters.
The proper, relaxed positioning of fingers, the proper humidity value, and the proper blood
circulation all might influence the result of the SPO2 recoring.
In details:
1. Blood circulation: proper blood circulation in the fingers is a condition of ECG recording. If blood
circulation is not proper, then the fingers are cold. In this case, please massage your palms and
fingers.
2. Humidity: to have a proper humidity is also important. If the fingers are too dry, please make your
fingers slightly wet.
3. Relaxed positioning of arms and fingers:
- please place the WIWE on the table and place your index fingers on the sensors in a way that your
wrist and even your elbow is supported by the table, and palms are relaxed close to the WIWE. This
is the most effective way of having a relaxed positioning of arms and fingers.
- do not press the sensors – it is totally enough only to touch the sensors with your fingertips (the
very end of your fingers, where the stimulus is the most effectively detectable).
- try to touch the sensors with the biggest possible surfuce of fingertips
- be sure that the fingers of your left hand does not touch the fingers of your right hand.
If you try to fix your fingers that way, that will most probably help to develop your technique of
measuring and you will get the needed results.
If you have the chance to give further feedback on the above points, that would be appreciated.
2. WIWE owner account and pedometer setting: click here
3. What you need to do if you experience issues in the performance or functioning of the device
There are two developer functions that are good to be aware of:
- Hard reset: press and hold the I/O button for 10 seconds to reboot WIWE if you experience connectivity issues, or the device freezes
- Data deletion: plug your WIWE device to a computer via a micro-USB charger and press the I/O button 5-10 times in quick succession
The WIWE is designed for long-lasting, proper performance. If you have any complaints, please contact our Customer Service. (info@myWIWE.com).
Sudden Cardiac Arrest is a life threatening disease, which might lead to death without quick and professional interventions. It can occur because of a previous heart disease or even without any sign as well. There is maximum 1 hour between the appearance of the first symptoms and death.
Around 6 million people die because of Sudden Cardiac Arrest each year. The chance of survival is less than 1 % worldwide!
Causes (you can learn more about heart diseases here):
- some inherited heart diseases
- heart coronary diseases
- arrhythmias
- stress, physical and psychic strain can also cause it without having any recognized heart disease
Possible signals of Cardiac arrest are tiredness, breathlessness or chest pain.

The aforementioned causes can lead to the weakening of the heart’s pumping function, which causes fibrillation and eventually Sudden Cardiac Death. In this process time is the most important factor. After Sudden Cardiac Arrest, blood circulation can be restarted by cardiopulmonary resuscitation within 5 minutes (probably without cerebral damage). After 5 minutes the damage of the brain is probable, while over 10 minutes the chance of survival is very low.
 If there is a suspicion of Cardiac Arrest, and you could help the individual, call immediately the ambulance and apply the steps of cardiopulmonary resuscitation-even as a lay person: clear the airway, do chest compressions and apply rescue breathing. With continuous chest compression we can gain some time until the medical personnel arrive. To restart the heart they use electric defibrillator.
If there is a suspicion of Cardiac Arrest, and you could help the individual, call immediately the ambulance and apply the steps of cardiopulmonary resuscitation-even as a lay person: clear the airway, do chest compressions and apply rescue breathing. With continuous chest compression we can gain some time until the medical personnel arrive. To restart the heart they use electric defibrillator.
 The cause of this disease is the lack of oxygen and nutrition in the brain. Normal blood supply of the brain is blocked by a clot coming from the heart or due to aortic stenosis of neck or brain.
The cause of this disease is the lack of oxygen and nutrition in the brain. Normal blood supply of the brain is blocked by a clot coming from the heart or due to aortic stenosis of neck or brain.
Stroke happens in the brain but effects the whole body. Due to the lack of oxygen, the functioning of certain parts of the brain and corresponding parts of the body stops.
Considering its development we can distinguish 2 types: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke
The cause of ischemic stroke (stroke due to lack of oxygen) is an aortic obstruction. The clot can develop either in one of the arteries (thrombosis) or in another part of the body and gets to the cerebral area (embolic stroke) blocking a smaller blood vessel and causing stroke. In 80 % of the cases strokes are of this type. It is important to know that atrial fibrillation (you can learn more here) is the main cause for heart-related stroke which can be detected by devices.
Hemorrhagic stroke
In this case the cerebral artery ruptures and bleeds, and the blood and oxygen cannot reach the tissues. Furthermore the blood can damage brain cells, resulting in increased pressure in the brain. The pressure that builds up in the brain can compress intact brain areas, or it may impede sufficient blood flow. Arteriosclerosis and high blood pressure are risk factors in the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
TIA (Transient ischemic attack)
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is often labeled as “mini-stroke”, because it is a temporary disorder of cerebral circulation (due to a blockage), often prior to stroke. It is also caused by a clot; the only difference between a stroke and TIA is that with TIA the blockage is transient (temporary). This group of symptoms occur rapidly and last for a relatively short time. That is why it is often ignored, although it can be a signal to a more serious stroke. With proper treatment of the symptoms, the stroke can be prevented.
On a yearly basis, 15 Million people get struck by stroke in the world. Out of them 6 Million dies and another 5 Million becomes permanently disabled. Stroke is the second leading cause of death among people over 60 and the 5th one in case of people between 15-59 years.
We can’t change a part of the risk factors, such as age, gender and family case history. The prevalence of cerebrovascular diseases and the underlying heart disorders (infarct, arrhythmia, you can learn more about heart diseases here) increases with age. Men over 40 and women over 50 are subject to significant risk for developing the above-mentioned diseases.
The other part of risks depends on the individual, and therefore stroke can be avoided. These factors are high blood pressure, obesity, lipid metabolism disorders, smoking, etc. Amongst these high blood pressure carries the biggest threat.
When stroke occurs, each minute counts! If you experience signals of a possible cerebrovascular catastrophe, call the ambulance without hesitation. The number of death and disabilities caused by stroke can be decreased if the patient gets to a specialist, and the cause of the cerebrovascular catastrophe gets stopped in time (within 3 hours from the first symptoms) with the help of certain examinations. In this case there is a chance, even for a total recovery.
Everyone knows about heart diseases. But do we know which diseases are we talking about exactly?
Heart diseases have 3 main groups: congenital heart diseases, inflammatory heart diseases and coronary heart diseases.
1. Congenital heart diseases
One in every 100 new-born baby has congenital heart disease, the majority of these can be cured by operation. A fetus has a heart similar to one-hollow shaft. It undergoes the fastest evolution at the age of four-eight weeks, therefore this is the most critical period considering the development of congenital heart diseases.
Besides genetic factors, the causes of congenital heart diseases are infections during early pregnancy (e.g. rubella), nutrients/materials causing malformations, lack of oxygen or ionizing radiation. Its symptoms are shortness of breath during physical strain, arrhythmias, suspicion to inflammation of the endocardium, the lips, the nails and the skin becomes cyanotic, the base of the nail becomes thicker, increased number of red blood cells and tiredness.
The different defects in the case of congenital heart diseases are atrial and ventricular septal defects, transposition of the great vessels, tetralogy of Fallot, persistent truncus arteriosus, etc.
2. Sore heart diseases
The wall of the heart consists of three different parts: endocardium, myocardium and pericardium (you can learn more about our heart here). Depending on which part of the heart flares up, we can talk about endocarditis, myocarditis and pericarditis.
The cause of these diseases can be virus, bacteria, parasite, fungus, allergic reaction and autoimmune disease.

Endocarditis is the inflammation of the inner layer of heart and heart valves because of the reproduction of the microorganisms in blood. If it is not treated in time, heart valves can be injured irreversibly. Other dangerous aspect of the disease is that the vegetation of the microorganisms can come off and travel with the blood blocking smaller veins or causing thrombosis.
Symptoms: fever, muscle and joint pain, loss of weight, sweating, weakness of limbs, paralysis, sight and speech disorder, strong headache, tiredness, choking, stomach pain on the left side of the body, chills, weakness, etc.
It can be treated with antibiotics or heart operation.
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is the inflammation of heart muscle (you can learn more here). It is mostly caused by common viruses and decreases heart’s functioning.
Symptoms: in case of mild inflammation it can be without any symptoms or in more severe cases it can cause fever, chest pain, heart failure and even sudden death. Symptoms in case of infants tend to be nonspecific, such as malaise, poor appetite, chronic cough, etc.
Treatment: primarily you should rest more and intake less salt, secondarily medicinal treatment, hospitalization or in the most severe cases implantable defibrillator.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the fibrious sac surrounding the heart, the pericardium. In most cases it is caused by virus infection. Through this process liquid gets into the layers of the pericardium threatening the normal functionality of the heart.
Symptoms: sharp chest pain, which is worse in the supine position or upon breathing in, fever, chills, muscle pain, all of these can radiate to the back, neck or the arms.
This disease can only be treated with medications.
3. Coronary artery disease
In case of these diseases the coronary arteries which nurture the heart are narrowed or calcified. Through this the oxygen saturation of the heart gets injured.
There are two types of coronary artery diseases: the angina pectoris and the myocardial infarction. The lack of oxygen can also cause cardiac failure, arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death (you can learn more here) too.
Angina pectoris
The angina pectoris is a syndrome that is caused by the ischemia of the heart muscle mostly through the obstruction of the coronary arteries.
The main symptoms is the discomfort of the chest, a squeezing, burning sensation, other than that there is breathlessness, sweating, pain throughout the upper parts of the body. These symptoms are augmented when moving.
Nytroglicerin can treat the disease, it can also immediately ease the symptoms. Treatments can be medicines, bypass operation or the widening of the artery.
Myocardial infarction
This is a more severe type of coronary artery diseases which cause is the damage to the heart muscle. It involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque which leads to the complete blockage of a coronary artery (you can learn more about our heart here). This leads to chest pain and discomfort. Symptoms are chest pain which radiates to other parts of the body. This pain is the most often described as a sensation of squeezing, pressure or tightness. The disaese can also cause shortness of breath, sweating, nausea or faint.
Treatment mainly involves the change of lifestyle, percutaneous coronary intervention or in the case of angina pectoris medicinal treatment.
The patient’s lifestyle greatly affects the development of myocardial infarction. The risk factors originating from it are smoking, obesity, lack of exercise and stress.
4. Cardiac Arrhythmia
We can talk about cardiac arrhythmia, when the heart doesn’t function properly, beating too fast, too slow or irregularly.
The risk factors that increases the chance of arrhythmia’s development are as follows: diabetes, high blood pressure, smoking, too much caffeine, too much alcohol, stress, drugs. The main causes of arrhythmia are scarred heart muscle (you can learn more here) after a myocardial infarction, heart valve or coronary artery disease, thinner walls of the atria.

In most cases there is an abnormal awareness of heartbeat, called palpitations, which can be frequent, infrequent or continuous although some of them aren’t necessarily harmful. Some arrhythmias do not cause any kind of symptom, but some of these are associated with adverse events.
It can be treated with medicines or a pacemaker.
5. Heart failure
This heart disease occurs when the heart can’t pump enough blood (you can learn more here about our heart) to suffice the needs of the body. It can develop if either the structure or the functioning of the heart gets damaged. It can affect either half of the heart or both. Although, it always originates from the left half of the heart, from the left atria.
Systolic dysfunction is the more readily recognized one. It is the failure of the pump function of the heart caused by the decrease of the ventricular contraction.
Diastolic dysfunction is described as the failure of the ventrical to relax resulting in a stiffer ventricular wall which causes inadequate filling of the ventricle.
There are different symptoms depending on which type of heart failure are we talking about. The main symptoms are shortness of breath, orthopnea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea in the case of the left-sided heart failure. In the case of right-sided heart failure the symptom is mainly edema starting from the ankles.
Treatment can be medicinal or by operation.
Healthy nutrition
The main cause of premature death is the development of cardiovascular diseases. The way of living, mostly the nutrition has a leading role in the development of such diseases.

Although there are threatening risk factors, which we cannot influence, we can have effect however on the factors related to our way of living, e.g.: amount of fat, cholesterol, salt, amount of fibre taken in daily.
Nutritional guide
The simplified figure of healthy nutrition is the nutritional guide, which has 3 typical forms: house, pyramid or rainbow type. We explain the pyramid type.

The base of the pyramid consists of foods that need to be a consumed in the biggest proportion. Cereals and foods made of cereals (of whole grain) belong to this group.
On the second level are the vegetables, vegetable dishes and fruits. It is suggested to eat from these 3-5 times a day to maintain our health.
Foods rich in protein are placed on the 3rd level of the pyramid, e.g.: meat, fish, milk, milk products and eggs.
On the top of the pyramid are the sugary foods. It’s best to eat the least out of these to protect our health.
In several nutritional guides egg is not listed in either of these levels because of the fact that it might increase the blood’s bad cholesterol. According to a study carried out by EUFIC (European Union Food Informational Council), the blood cholesterol is increased mainly by the quantity and quality of consumed fat and the cholesterol intake has a much lesser effect on it. On the other hand, egg is a great source of protein, vitamins and minerals.
Besides nutrition, vitamins and minerals that supply the body with energy, the body needs water as well. 2-2, 5 liters of liquid is needed, primarily in the form of water, mineral water or juices.
Unprocessed or cooked?
 Besides choosing the right kind of foods we have to care about the method of intake, aiming to have the most possible amount of nutriment taken in. So we have to consider to eat our food either unprocessed or cooked. Both methods have its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s see some tips which help us find the optimal solution:
Besides choosing the right kind of foods we have to care about the method of intake, aiming to have the most possible amount of nutriment taken in. So we have to consider to eat our food either unprocessed or cooked. Both methods have its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s see some tips which help us find the optimal solution:
- When we have the choice, it’s best to eat vegetables and fruits unprocessed (fresh and ripe) because this will preserve the whole food value.
- If you have no unprocessed foods available, instead of tinned food, choose the frozen foods.
- Decrease the amount of fat by using less dressing rich in mayonnaise.
- When you boil the vegetables, don’t waste the water in which the valuable vitamins and minerals are.
- Potatoes are suggested to be boiled, baked with its peel, or pleated instead of cooking in oil.
- Instead of white rice use brown rice, which contains more fibre (the only disadvantage of boiling brown rice is that it needs more water and more time).
How to decrease cholesterol
It is an essential question how much fat we use to prepare our food, because it has effect on the cholesterol level of our body. To decrease the amount of fat, instead of frying, cook in kitchen film, crockery, micro, on grill or boil the food.  As an effect of bad cholesterol, there can be a thickening plaque layer on the wall of blood vessels which impedes the flood of blood. This might increase blood pressure and the risk of heart diseases.
As an effect of bad cholesterol, there can be a thickening plaque layer on the wall of blood vessels which impedes the flood of blood. This might increase blood pressure and the risk of heart diseases.
The juice of pomegranate is a natural panacea, which protects from the increase of cholesterol and the development of plaque layers - drinking regularly the juice of pomegranate decreases the thickness of plaque layers in the wall of the blood vessels by 30 %. Eating pomegranate is efficient in the prevention of about 100 diseases besides the cardiovascular diseases. The beneficial effects of pomegranate are proved by a study testing people between 65 and 75 for 3 years. Its results have shown that the pomegranate course decreased the thickness of plaque layers in blood vessels by 60 %, and therefore decreased the bad cholesterol by 58 %.
Fish oil for your heart’s health
We have heard a lot about the beneficial effects of eating fish. But do we know why it is good? There is omega-3 fatty acid in fish, fish oil and vegetables, that decreases the chance of cardiovascular diseases.

Omega-3 fatty acids have 3 types: the multiply-saturatedalpha-linolenic acid (ALA), the eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Especially the DHA and EPA have good effects on our body. This is proved by a research carried out among eskimos in Greenland.
 Eskimos eat abundant fat of sea animals, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These decrease the amount of triglycerides, heart rate, arteriosclerosis and blood pressure. Thanks to these facts, the cardiovascular diseases are practically unknown among eskimos.
Eskimos eat abundant fat of sea animals, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These decrease the amount of triglycerides, heart rate, arteriosclerosis and blood pressure. Thanks to these facts, the cardiovascular diseases are practically unknown among eskimos.
The recommended daily intake of omega-3 fatty acid is 1,6 gram/day for men and 1,1 gram/ day for women. But be careful with the consumption of omega-3 fatty acid if you have a developed heart disease. In this case the allowed daily amount is 1 gram. Here is a list of foods that contain omega 3 fatty acid: fishes in different forms (sandwich creams, baked, grill or salad); tofu, soy, rape, linseed, nut. For those who does not like fishes or cannot eat the recommended amount, the fish oil capsule is recommended as an alternative solution.
Using salt and sugar
Using honey, or artificial sweeteners for cooking help us to moderate our sugar intake.
Consuming too much or too low amounts of salt both has bad effects on our health. To eat proper amount of salt, use less of it when preparing foods. Use fresh or desiccated herbs, substitute the salted, tinned foods with fresh foods instead.
 Recommended diet to protect your heart
Recommended diet to protect your heart
The factors in the development of heart diseases are gender, age, genetic makings, obesity, diabetes, not enough physical activity, untreated high blood pressure, high fatty –acids level, smoking and stress. When there are more factors present, the risk is much higher.
That is why the main purpose is to decrease risk factors. In case of developed heart diseases or other cases the post preventive acts are necessary to avoid aggravation of damage in organs and blood vessel mutation. This is the work of the doctors taking part in rehabilitation and also the change in the way of living and the making of a healthy meal plan.
Workout of healthy meal plan
Myocardium is the muscle responsible for heart contractions, built up of striated muscle filaments. These muscle filaments are able to do quick contractions and continuous movements (you can learn more here about our hearts structure).
The heart muscle is one of the three major types of muscle (the other two types are skeletal and smooth muscle). Heart muscle has a striped structure, just like skeleton muscles, while its nucleus is centralized similarly to smooth muscles.
Factors related to the endurance of the heart muscle are the following ones:

- mithocondrions are able to execute aerobe breathing by means of oxidative phosphorization
- a great number of myoglobin can be found in it
- has an excellent blood flow
With the help of these characteristics heart muscle is able to supply brain continuously with oxygen and nutrients. Heart is attuned to aerobe breathing which results in not being able to pump enough blood in case of ischemic status.
Normally, energy comes from fat in 60 %, carbohydrates in 35 % and amino acids and ketone in 5 %. This ratio may vary depending on the nutrition supply.
Cardiomyopathy is a definition for all those heart diseases (you can learn more here) that develops due to the failure of the heart’s pumping function. Cardiomyopathy can be divided into subgroups featured by the type of disorder. Symptoms vary in case of each types, and therefore we can draw conclusions regarding the cause of problem and we can also choose the specific treatment on the basis of symptoms which vary by 3 main types.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
The thickening of the heart muscle is the cause of this disease, which will impede the proper working of valves and block the circulation of blood. This type is often congenital.
Symptoms:
- dizziness
- fainting
- pain in the chest
- breathlessness in case of physical loading
- often arrhythmia
Dilated cardiomyopathy
In this case the heart muscle elongates and therefore the heart becomes enlarged. This common heart disease can reach a very serious or even fatal status. Due to enlargement, myocardial force decreases and therefore the heart will be unable to pump enough blood. (you can learn more about ECG here)
Symptoms:
- tachycardia
- breathlessness
- pale, coolish and sweltering (because of malfunctioning circulation)
- moodiness
- asitia
- nausea
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
In this kind of cardiomyopathy the walls of the Left Ventricle are rigid, and the heart is restricted from stretching and properly filling with blood.
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
A rare kind of cardiomyopathy which causes the enlargement of the Right Ventricle and the disorder of the Right Chambers of the Heart. It is caused by a genetic defect.
Treatment
Primarily the arrhythmia can be cured by medicines or by implanting a pacemaker.
In case of Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the enlarged part of myocardium can even be removed by surgery.
In the majority of dilated cardiomyopathy cases, medicine treatment is used for decreasing the strain and increasing the heart muscle’s functioning.
It is important to know that these diseases cannot be cured, these are only treatments of the symptoms. The nearly original status necessary for the proper functioning of the heart muscle cannot be restored. Thickening or weakening of the heart muscle is irreversible.
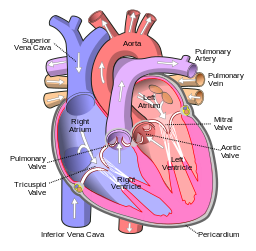
Parts of our heart
Heart is covered by a double-layered heart membrane called pericardium. On the outer surface of pericardium, the borders of the heart chambers and the coronary network are visible, which are responsible for the nourishment of the heart. The primary funcion of pericardium is to protect the heart and fix it to the breastbone, spine and other parts of chest cavity by the means of ligaments.
In the inner side of pericardium we can find the heart wall, which consists of 3 histological layers. The outer one is the single-layer endothel. Under that there is the myocardium (you can learn more here), which is built up of special muscle tissues, called cardiac muscle. The inner, third part is the endocardium, which is a membrane of connective tissue.
The interior of the heart has left and right side separated by a thick, muscular wall called septum. Each side has an upper chamber called atrium and a lower chamber called ventricle, divided by valves. Atrias are smaller than the ventricles, and their walls are thinner. Their job is to hold the blood before it goes down to the ventricles. The ventricles are bigger and have thicker muscular walls (3 layers of muscle). Their job is to pump the blood. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs, while the left ventricle pumps blood to all other parts of the body. For this reason, the left ventricle has a thicker muscular wall. For the best, continuous circulation, the heart muscles are wrapped around ringwise.
The Atrium Dextrum is an oval hollow, its inside wall is partly smooth (sinus venosus), partly reticulated (Atrium Primitivum). Blood low in oxygen from the systemic circulation enters the right Atrium from the Superior and Inferior Vena Cavae and passes to the Right Ventricle. The Superior Vena carries blood from the upper parts of the body (head, neck, upper limbs), while the Inferior Vena Cava carries blood from all other parts of the body. On the border of the Right Atrium and Right Ventricle (Ventriculus Dexter) is the Ostium Venosum Dextrum, which binds the 2 parts together. The Sinus Coronarius – which collects the blood of the heart- enters into the Right Atrium between the Ostium Venosum Dextrum and the inflow of Vena Cava Superior. The Right Atrium is situated on the breast, fitted together with the breastbone and ribs. Its cross-sectional picture is a half-moon, and sorrounds the Left Atrium. It has a thickness of 5 mm. Between the Ostium Venosum Dextrum and Right Atrium is the Valvula Tricuspidalis, which ensures that the blood flows into one direction.
Valves join to the Musculi Papillares by means of Chordae Tandineae. There are the three half-moon-shaped Valvula-semilunaris by the hole of Arteria Pulmonaris, which is coming from the Ostium Arteria Dextrum of Right Ventricle. The perfect insertion of Valvula Semilunaris assists the one-way flow of blood.
The structure of Oval Atrium Sinistrum is similar to the Atrium Dextrum. This is situated on the back side of the heart. The blood rich in oxygen enters the Left Atrium from 2-2 Vena Pulmonalises. The left side of the heart is divided into two parts by the Ostium Venosum Sinistrum. The blood gets through this from the left Atrium to the Left Ventricle. Valvula bicuspidalis is situated on the verge of the Left Atrium and Ostium Venosum Sinistrum. Left Atrium has a very similar structure to the Right Atrium, but its wall is much thicker (approximately 10 mm). The main Artery of our body comes from the Ostium Arteria Sinistrum which is closed by 3 half-moon-shaped valves. The Arteria Coronaria derive from the wall of Aorta and Valves, these are called Right and Left Sinus Valsavae. These Coronary Arteries provide heart with blood. Heart attack happens when Coronary Arteries are blocked. The Fossa Ovalis is a nook situated along the Septum, between the Right Ventricle and Left Ventricle, which is remanence from the fetal circulation.
The functioning of heart
Blood from the lungs and the body arrives to the left and right Atriums and flows towards the Ventricles, then they pump the blood to the lungs and to the whole body again. The right side of the heart is responsible for pumping deoxigenated blood (blue) coming from the body, while the left side of heart pumps the oxigenated blood (red) coming from lungs.
The oxigenated blood and deoxigenated blood cannot get mixed, because there is the Septum (separating wall) between the Atriums and Ventricles. The Septum prevents the two different kinds of blood to get mixed.
The process of blood circulation:
Deoxigenated blood arrives to the Right Atrium from the body through two big veins. Blood goes to the Right Ventricle through the Tricuspid Valve, and the heart pumps the blood to the lungs from here. Deoxigenated blood arrives to the lungs, where it gets oxygen and goes back to the Left Atrium through the left and right Pulmonary Arteries. From here, blood gets to the Left Ventricle through the Mitral Valve, which pumps the oxigenated blood through the Aorta back to the body.
Electrocardiography is the process of non-invasive medical recording, showing the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on the patient's body. These electrodes detect electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.
The heart contraction takes place due to an electrical stimulus. This normally derives from the sinoatrial node, and spreads to heart muscle cells through a special electrical conduction system. ECG is able to measure this with electrodes placed on the patient's limbs and surface of the chest. In this way the recorded electrical signals will draw the ECG wave, which is a regular curve with unique characteristics.
ECG -called also Einthoven-type diversion - was invented by Willem Einthoven (1860-1927), a Dutch physiologist. He was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery in 1924. His discovery and observation is correct even up to this day.

Twelve-lead ECG of a 26-year-old male
The purpose of ECG
The purpose of an ECG recording is to examine the spread of the heart’s electrical potential. The following parameters can be analyzed by ECG:
- heart rhythm
- the starting point of stimulus
- velocity of electrical conduction
- thickness of myocardium
- possible disorder in the circulation of myocardium
ECG recording
During ECG recording (you can learn more here about recording with WIWE) we can draw conclusions regarding the status of the heart by examining its electrical activity. Electrical signs are gathered together by the electrodes placed on the limbs and precodial area. In case of the 12 lead ECG there are 4 limb electrodes and 6 precodial electrodes. The ECG produces 6 leads (I, II, III, aVF, aVR, aVL) with the information coming from the 4 limb electrodes, while the 6 precardial electrodes are equivalent to the other 6 leads (V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6). The purpose of different leads is to show the heart from different sides. The 12 leads provide us a reasonable number of directions, which lets us have an overall picture of our heart. For research purposes applying 100 or even more leads can be reasonable.
ECG curve
The waves recorded by ECG, namely P; Q; R; S; T; and U are integrated international notations. Each wave defines the depolarization or repolarization of the different parts of the heart during its functioning.
- P-wave (atrial wave): The p-wave represents depolarization of the atria. It has positive amplitude of 1-2 mm. Its duration is 0,06-0,11 sec.
- P-R Interval: This interval reflects the time the electrical impulse takes to get from the sinus node through the AV node. Its duration is 0,04-0,1 sec.
- QRS complex: The QRS complex represents the rapid depolarization of the right and left ventricles. The complex consists of a negative Q-wave, which is not always recognizable, a high positive R-wave, which is the electrical polarization of muscle’s main mass (its amplitude is 10 mm) and a negative S-wave. Depolarization of Ventricles’s whole muscle takes place during the running of QRS complex. Its total duration is 0,06-0,1 sec of which 0,03 is the depolarization is interventricularis septum, 0,055 sec is the depolarization of the Right Ventrical and 0,068 sec is the depolarization of the Left Ventricle.
- ST interval:it represents the period during which the ventricles are repolarized.
- T-wave: a long-drawn wave of middle amplitude, shows the total repolarization of ventricles, its duration is 0,2 sec.
- Q-T interval: the total duration of depolarization and repolarization in the ventricle’s muscle.
- U-wave: The U wave is hypothesized to be caused by the repolarization of the interventricular septum or the ventricles. Its duration is 0,1-0,2 sec.
Heart rhythm, sinus rhythm
We need to examine the number of heart beats in case of a chosen lead to be able to identify the heart beats securely. This is usually the II. lead (WIWE uses lead I, you can learn more here). To discover arrhythmias we need at least 12 or more sequential cardiac cycles.
Normal heart rate is called sinus rhythm, during which the sinusnode acts as a natural pacemaker.
The parameters of sinus rhythm
- 60-100 heart beats per minute
- P -wave has a positive amplitude in the II. lead, and negative in the VR
- QRS complex comes after the P –wave every time
In case of Atrial fibrillation the operation of sinus node, which secures the regular rhythm of the heart fails and an irregular electrical activity controls the heart contractions. As a consequence, the ventricles contract too quickly and irregularly.
Atrial Fibrillation without treatment can cause serious intergrowth, like cardial failure and stroke, which are the most serious outcomes. Stroke (you can learn more here) can develop as a result of a clot coming from the heart or embolism. It may origin from the Left Atrium orAtrial Appendage. Atrial Fibrillation can multiple the risk of stroke by 4-5 times.
33, 5 million people suffer from Atrial fibrillation worldwide, which is 0,5 % of the whole world’s population. The chance for the development of Atrial Fibrillation is 2,3 % over the age of 40, while this goes up to 5,9 % over the age of 65. In 70% of the time people suffering from this disease are between the age of 65 and 85. Also, men are more susceptible to the disease.

Normal rhythm (left) Atrial fibrillation (right);
Factors which increase the chance of Atrial Fibrillation (you can learn more about heart diseases):
- Hypertension
- Coronary artery stenosis
- Mitral valve disease early after heart operation
- Congenital heart disorder
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary cancer
- Pulmonary embolism
- Hyperthyreosis
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Typical symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation:
- Irregular and quick palpitation
- Tiredness
- Breathlessness
- Dizziness
- Pain in the chest
In certain cases, Atrial Fibrillation can be totally free of symptoms. In these cases the disease can only be diagnosed by a routine medical examination.
According to the European Heart Rhythm Association the seriousness of symptoms is separated into 4 stages.
Types of Atrial Fibrillation:
- Arrhythmia recognized promptly
- Recurring, 2 or 3 times
- Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: arrhythmia spontaneously ceases within 2-7 days.
- Persistent Atrial fibrillation: lasts for more than 7 days.
- Long persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Atrial Fibrillation lasts for more than a year.
- Permanent Atrial fibrillation: when arrhythmia lasts for a lifetime. In this case regular heart beat cannot be permanently re-established.
Possible monitoring methods of Atrial fibrillation:
• Physical monitoring
If irregular beating is recognized by feeling the pulse it might be the sign of arrhythmia.
• ECG (you can learn more here)
This is the basic tool for detecting the arrhythmia. If there is Atrial fibrillation, the P-waves will not appear on the ECG curve, and the contractions will be irregular.
• Echocardiography
It can help to identify valvular heart disease, analyze pumping function. Thrombus is also detectable with it in the chambers of the heart.
• Lab test
Examines the function of thyroid, kidney and liver.
• Holter ECG
Electrodes are placed on the surface of the body to record the electrical potential of the heart. Such continuous monitoring may help to reveal arrhythmias.
• Transesophageal echocardiogram
This method is able to detect the presence of thrombus in the Left Atrial Appendage, which is a risk factor in the development of Atrial Fibrillation.
Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
There are many ways of treatment for those who suffer from Atrial Fibrillation. During treatments the primary purpose is to decrease the thromboembolic risk by using anticoagulant. After that it has to be decided whether to attempt the re-establishment of the regular sinus rhythm or try to keep the heart frequency in check.
Treatments to restore heart frequency
Electrical cardioversion
In this case the regular rhythm is restored by electrical impulse by the means of electrodes. Electrodes are placed on the chest of the properly prepared patient under a short anesthesia.
Catheter ablation
In this process radio frequency energy is used to fracture the source of an irregular stimulus or block its spreading.
Prospects, prognosis
In the presence of Atrial fibrillation, mortality and the number of further complications increase. The latter ones are:
- stroke (you can learn more here)
- thromboembolism
- cardiac failure
- failure in the functioning of Left Ventricle
- the extent of load capacity fall.
[14] ime_2017_PF_TubolyG
The WIWE device
WIWE is a measuring device which monitors your heart function and heart rhythm- at home or on the way. WIWE gives you information about the average heart rhythm, the possible deviation from the normal ECG (learn more) values and the level of oxygen saturation. It also has a built-in pedometer (learn more). You can take recordings with WIWE on its own, but its evaluation will be available with the help of a mobile application which is running on your smartphone.
Application: Evaluation on smartphone / tablet
The evaluation of measured data and their detailed representation is made by an application, which is free to download from the App Store for mobiles /tablets working with iOS system or Google Play for mobiles/tablets working with Android system.
How to do ECG recording
With the help of WIWE and the application you can take recordings. The measured data will be available on the evaluation screen of your smartphone /tablet and there is the possibility that you can share those with others (e.g. your doctor).

Before taking a recording:
Please pay attention to the topics below so that you get precise measured data:
- Sensors should get in touch with the skin of your fingertips directly.
- If your skin is too dry, make it wet with a watered piece of material before recording.
- If the sensors are polluted, remove it with a clean, soft piece of material from it surface.
- During recording do not touch the other parts of your body with your hands.
- Please be sure that the skin of your hands will not touch each other, and that neither you or the sensors of the device do not touch any conductive device. Otherwise recording cannot be taken correctly.
- During recording do not move, speak and hold the device still. Any movement can result in incorrect recording.
- Recoding should be taken in a sedentary position, rather than standing.
A) The recording (normal recording) using (learn more) phone
1. Push the I/O button to switch on the device.
2. Start recoding by placing your „left hand”-„right hand” thumbs on the device- as shown in the application.
3. Successful recording starts with a preparation period, during which you need to hold your thumbs on the sensors of WIWE device and stay relaxed. During preparation period application controls if the contact between the sensors and thumbs is correct, and that data coming from WIWE are suitable for the start of recording, or not.
4. On the WIWE device, the process indicator LEDs show the grade of recording.
5. Data collection during recording takes minimum 30, maximum 60 seconds, meanwhile the application indicates ECG signal, heart rate and the level of blood’s oxygen saturation.
6. If you release the sensors within 30 seconds, the recording gets interrupted.
7. After 60 seconds the application indicates that you can release the sensors and the data collection is over.
8. To make the evaluation, the application needs some seconds. After that the results will appear on the evaluation screen.
9. In case of an unsuccessful recoding, follow the instructions of your application and repeat the recording.
10. During the recording the flashing error LED shows that the ECG signals are unstable or too weak. In this case repeat the recoding.
11. The device will start recording only if the battery level is high enough for taking at least 1 recording.
The causes of inaccurate recording
- Contact between sensors and fingers is not direct enough.
- During recording there is contact between the skin of your hands.
Results
After recording and evaluation the measured data will be available on the evaluation screen of mobile in numbers and graphs. Results are suggested to be sent to your doctor, as well, so that any disorder get revealed on the basis of measured data.

The 3 circles on the screen correspond to 3 measured characteristics: ECG (electrocardiogram); AR/AF(Arrhrytmia/ Atrial Fibrillation); VH ( Ventricular Heterogeneity).
The colours of circles can vary from green, yellow and red depending on the evaluation of the measured data:
Green= normal status
Yellow= slight deviation from the normal status
Red= severe deviation from the normal status
Touching the circles, the undermentioned information can be reached:
ECG: Shows the degree of deviation from normal ECG parameters (depending on its colour it can be normal, slight, or severe).
AR/AF: This function is meant to monitor the regularity of the heart rhythm and detect the signs of atrial fibrillation (learn more about it here) to give you feedback on the regularity of your heart rhythm and any possible irregularities occuring in it.
VH: The figure indicating the condition of the heart muscle (learn more about it here), the degree of ventricular heterogenity (VH) which can be (indicated by the fill color): green (normal/healthy), yellow (showing a slight deviation, elevated VH) , or red (showing a severe deviation, highly elevated VH)
Below the circles are the SPO2 and Bpm buttons, which indicate the values of oxygen saturation and heart rate.
SPO2: The oxygen saturation of blood indicated in %. The measured value appears on a runner which is placed under the value of measured result. The colour of runner shows the degree of acceptability.
Bpm ( bit per minute) : The number of pulse rate in a minute; (normal, possible, probable). The measured value appears on a runner which is placed under the value of measured result. The colour of runner shows the degree of acceptability.
Touching the Details button on the right lower side of screen we can have more detailed measurement data.
- ECG parameters (you can learn more here): The graph of aggregated majority circles, showing the relevant HR, QRS, QTc and PQ data and reference values, as well. A red exclamation mark indicates the differences next to each types of data.
- ECG curve: the ECG curve of the measured data, where pages can be turned along the length of recording and enlargeble fourfold maximum.
- Arrhytmia examination: a Poincaré graph that monitors the regularity of the heart rhythm and looks for the signs of atrial fibrillation based on the number of clusters and their dispersion around the diagonal.
- Ventricular heterogenety: used for the evaluation based on two parameters: the avarage VH and its dispersion. Based on our algorithm you result gets classified into one of the different color coded areas.
Notes related to recording: Notes can be added to each recording. The remarks concerning the circumstances of recording – e.g. medicines taken in- can help the doctor evaluate the measured data and set up accurate diagnosis.
Share the recording: There is a possibility to share your recordings with others in e-mail (with your GP or medical specialist). Detailed description can be found in the mobile application’s Information menu/ Detailed Instructions.
Access to previous recordings and evaluated results
You can follow the change of data related to the status of your health with the help of the health diary in the Data menu of mobile application,
B) Recording without using (you can learn more here) mobile (occasional recording)
In certain case the user’s mobile can be out of reach. There is possibility to take recording even in this case. Follow the instructions below:
- Switch on the device.
- Be sure that the error led is not on.
- Start recoding by placing your „left hand”-„right hand” thumbs on the device.
- On the WIWE device, a process led shows if the recording has started and the grade of recording.
- Wait till the last of the WIWE’s process led becomes green.
- Then the recording is over, WIWE stores the results of recording till the next synchronization with your mobile.
- The error led will flesh if any mistake occurred during recording. In this case please repeat the recording.
Synchronization
During synchronization via Bluetooth the measured data get loaded between the user’s default WIWE device and mobile, if the connection between the mobile and WIWE device is already set up.
Synchronization is needed because the ECG recording and pedometer (you can learn more here) function of WIWE operates independently of application, and data is stored in the memory of WIWE till it gets loaded to the mobile by the synchronization. Application will inform you about successful or unsuccessful synchronization. By means of a successful synchronization the data stored on the WIWE device – after they are saved on the mobile- get cancelled. In case of unsuccessful loading, synchronization need to be repeated.
You can order WIWE from our webshop or buy directly from our distributors whose list you can view here
No, you won’t need to get a prescription to purchase WIWE.
Igen, az együttműködő pénztárak listáját itt találja: Egészségpénztárak
No, unfortunately it won't.
You can find the list of compatible phones/tablets here.
In case of Android devices you’ll need Android Lollipop 5.0 or newer.
In case of Apple devices you’ll need iOS 8.1 or newer.
Az applikáció alapvetően mobiltelefonok képernyőjére lett optimalizálva, de táblagépekkel is használható, a képernyő megjelenítésében lehetnek apróbb, funkciókat nem akadályozó hibák. Egyelőre nem elérhető PC/laptop kapcsolódás lehetősége.
In our case ventricular heterogenity is the diversity of the ventricle’s heart muscle cells’ bioelectrical property. This heterogenity is present even in healthy cases as predetermined (basically tense connection between the cells). But, in pathological cases the heterogenity of the cells grow and the aligned working of the heart muscle cells becomes worse. This calls forth the lability of the bioelectrical phenomenons. This instability increases the risk for developing dangerous ventricular arrhythmias, hereby increasing the risk for Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
WIWE has been issued Class IIa CE mark in medical device category.
No, WIWE records single-channel ECGs and is not intended to be a replacement for a 12-lead ECG.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest is the unexpected stop of the beating of the heart. Because of this, the blood can’t reach the brain and other vital organs in the body. If this condition doesn’t get treated within minutes, it causes death, which is called Sudden Cardiac Death.
The data recorded will be stored on the users smartphone or tablet.
No, there are no known medical contraindications which could prohibit the use of WIWE.